前几天有人问我如何升级glib库,并在各个版本之间切换。本想用rpm安装的,结果发现glib安装包不支持修改安装目录,如下图。
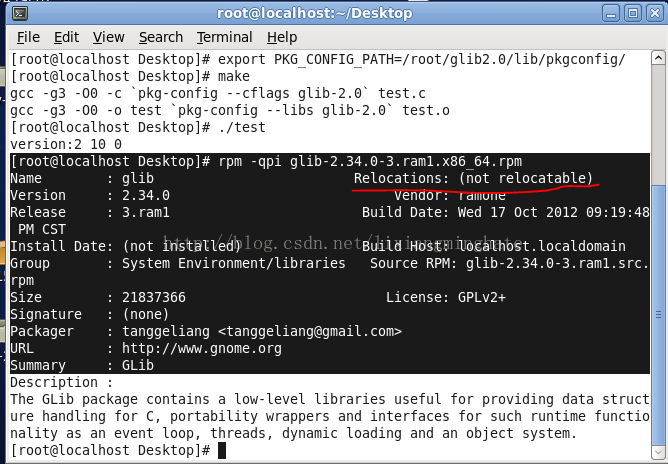
如此,只能在编译源码时指定安装路径了。其实,我这是为了演示升级才安装glib库,我本身不需要它,所以不要问我如何使用glib提供的功能。
首先下载了glib2.4(https://developer.gnome.org/glib/),解压后看看glib提供了哪些配置选项(都说只是演示库的升级,我并不想完整安装glib):
[root@localhost glib-2.4.0]# ./configure -help
`configure' configures glib 2.4.0 to adapt to many kinds of systems.
Usage: ./configure [OPTION]... [VAR=VALUE]...
To assign environment variables (e.g., CC, CFLAGS...), specify them as
VAR=VALUE. See below for descriptions of some of the useful variables.
Defaults for the options are specified in brackets.
Configuration:
-h, --help display this help and exit
--help=short display options specific to this package
--help=recursive display the short help of all the included packages
-V, --version display version information and exit
-q, --quiet, --silent do not print `checking...' messages
--cache-file=FILE cache test results in FILE [disabled]
-C, --config-cache alias for `--cache-file=config.cache'
-n, --no-create do not create output files
--srcdir=DIR find the sources in DIR [configure dir or `..']
Installation directories:
--prefix=PREFIX install architecture-independent files in PREFIX
[/usr/local]
--exec-prefix=EPREFIX install architecture-dependent files in EPREFIX
[PREFIX]
By default, `make install' will install all the files in
`/usr/local/bin', `/usr/local/lib' etc. You can specify
an installation prefix other than `/usr/local' using `--prefix',
for instance `--prefix=$HOME'.
For better control, use the options below.
Fine tuning of the installation directories:
--bindir=DIR user executables [EPREFIX/bin]
--sbindir=DIR system admin executables [EPREFIX/sbin]
--libexecdir=DIR program executables [EPREFIX/libexec]
--datadir=DIR read-only architecture-independent data [PREFIX/share]
--sysconfdir=DIR read-only single-machine data [PREFIX/etc]
--sharedstatedir=DIR modifiable architecture-independent data [PREFIX/com]
--localstatedir=DIR modifiable single-machine data [PREFIX/var]
--libdir=DIR object code libraries [EPREFIX/lib]
--includedir=DIR C header files [PREFIX/include]
--oldincludedir=DIR C header files for non-gcc [/usr/include]
--infodir=DIR info documentation [PREFIX/info]
--mandir=DIR man documentation [PREFIX/man]
Program names:
--program-prefix=PREFIX prepend PREFIX to installed program names
--program-suffix=SUFFIX append SUFFIX to installed program names
--program-transform-name=PROGRAM run sed PROGRAM on installed program names
System types:
--build=BUILD configure for building on BUILD [guessed]
--host=HOST cross-compile to build programs to run on HOST [BUILD]
Optional Features:
--disable-FEATURE do not include FEATURE (same as --enable-FEATURE=no)
--enable-FEATURE[=ARG] include FEATURE [ARG=yes]
--enable-maintainer-mode enable make rules and dependencies not useful
(and sometimes confusing) to the casual installer
--enable-debug=[no/minimum/yes]
turn on debugging [default=minimum]
--enable-gc-friendly turn on garbage collector friendliness [default=no]
--disable-mem-pools disable all glib memory pools
--enable-ansi turn on strict ansi [default=no]
--enable-threads turn on basic thread support [default=yes] ([=no] will override --with-threads)
--disable-rebuilds disable all source autogeneration rules
--disable-dependency-tracking Speeds up one-time builds
--enable-dependency-tracking Do not reject slow dependency extractors
--disable-largefile omit support for large files
--enable-static[=PKGS]
build static libraries [default=no]
--enable-shared[=PKGS]
build shared libraries [default=yes]
--enable-fast-install[=PKGS]
optimize for fast installation [default=yes]
--disable-libtool-lock avoid locking (might break parallel builds)
--enable-included-printf
use included printf [default=auto]
--enable-gtk-doc use gtk-doc to build documentation default=no
--enable-man regenerate man pages from Docbook [default=no]
Optional Packages:
--with-PACKAGE[=ARG] use PACKAGE [ARG=yes]
--without-PACKAGE do not use PACKAGE (same as --with-PACKAGE=no)
--with-libiconv=[no/gnu/native]
use the libiconv library
--with-gnu-ld assume the C compiler uses GNU ld [default=no]
--with-pic try to use only PIC/non-PIC objects [default=use both]
--with-tags[=TAGS]
include additional configurations [automatic]
--with-threads=[none/posix/dce/solaris/win32]
specify a thread implementation to use
--with-html-dir=PATH path to installed docs
--with-xml-catalog=CATALOG
path to xml catalog to use
Some influential environment variables:
CC C compiler command
CFLAGS C compiler flags
LDFLAGS linker flags, e.g. -L<lib dir> if you have libraries in a nonstandard directory <lib dir>
CPPFLAGS C/C++ preprocessor flags, e.g. -I<include dir> if you have headers in a nonstandard directory <include dir>
CXX C++ compiler command
CXXFLAGS C++ compiler flags
CPP C preprocessor
CXXCPP C++ preprocessor
F77 Fortran 77 compiler command
FFLAGS Fortran 77 compiler flags
Use these variables to override the choices made by `configure' or to help it to find libraries and programs with nonstandard names/locations.
Report bugs to <http://bugzilla.gnome.org/enter_bug.cgi?product=glib>.
通过这个列表,可以选择性的编译glib的源码,以及设置编译参数,我的设置如下:生成静态库,不优化,生成映射文件
./configure --prefix=/root/glib2.4 --enable-debug=yes --enable-static CFLAGS="-g3 -O0" LDFLAGS="-Wl,-Map,Sym.map"
由于运气好,make 和make install过程没有出错,于是glib2.4 done
同样的办法用在glib2.10上,最终,我的电脑上有了两个版本的glib库:

安装库的目的是为了在工程中使用它提供的功能,因此此处写了一个测试程序test.c及Makefile:
###################
test.c:
#include <glib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("version:%d %d %d\n",GLIB_MAJOR_VERSION,GLIB_MINOR_VERSION, GLIB_MICRO_VERSION);
return 0;
}
###################
Makefile:
TARGET=test
OBJS=test.o
all:$(OBJS)
gcc -g3 -O0 -o $(TARGET) `pkg-config --libs glib-2.0` $(OBJS)
%.o:%.c
gcc -g3 -O0 -c `pkg-config --cflags glib-2.0` $<
Makefile中使用了pkg-config工具来管理库版本,做到自由切换库的目的。这里从网上摘抄一段对pkg-config的描述:
"pkg-config要求库提供一个.pc元数据文件,从这些文件中检索库的各种必要信息,包括版本信息,编译和连接需要的参数等。这些信息可以通过pkg-config提供的参数(如--cflags, --libs)单独提取出来直接供编译器和连接器使用。
默认情况下,每个支持pkg-config的库对应的.pc文件,在安装后,都位于目录/usr/lib/pkgconfig目录下。
环境变量PKG_CONFIG_PATH是用来设置.pc文件的搜索路径的,pkg-config按照设置路径的先后顺序进行搜索。这样,库的头文件的搜索路径的设置实际上就变成了对.pc文件搜索路径的设置。"
...
"一般来说,即使是使用同一个库,不同的用户在安装时也可能会安装在不同的目录下。这样在编译时使用-I参数指定include路径,在连接时使用-L参数指定lib库的路径,可能造成了编译,连接的不一致,同一份程序从一台机器copy到另一台机器时就可能会出现问题。
pkg-config就是用来解决编译连接界面不统一问题的一个工具。
它 的基本思想:事先把库的各种必要信息保存在.pc文件中,需要的时候可以使用参数(--cflags,--libs),将所需信息提取出来供编译和连接使用。这样,不管库文件安装在哪,通过库对应的.pc文件就可以准确定位,可以使用相同的编译和连接命令,使得编译和连接界面统一。
它提供的主要功能有:
<1> 检查库的版本号。如果所需库的版本不满足要求,打印出错误信息,避免连接错误版本的库文件。
<2> 获得编译预处理参数,如宏定义,头文件的路径。
<3> 获得编译参数,如库及其依赖的其他库的位置,文件名及其他一些连接参数。
<4> 自动加入所依赖的其他库的设置。"
这大段话提到了.pc文件,提供了编译连接的参数,那来看看我安装的两个版本的glib库的.pc文件:

左边是低版本2.4右边是高版本2.10。
最后来看下如何在编译时实现两个版本之间切换:
通过设置export PKG_CONFIG_PATH=path to .pc设置.pc文件的搜索路径并使用其中的编译连接参数。
如test使用2.4的库,则设置为:
export PKG_CONFIG_PATH=/root/glib2.4/lib/pkgconfig/
使用2.10的库,则设置为:
export PKG_CONFIG_PATH=/root/glib2.0/lib/pkgconfig/
最终的运行结果为:
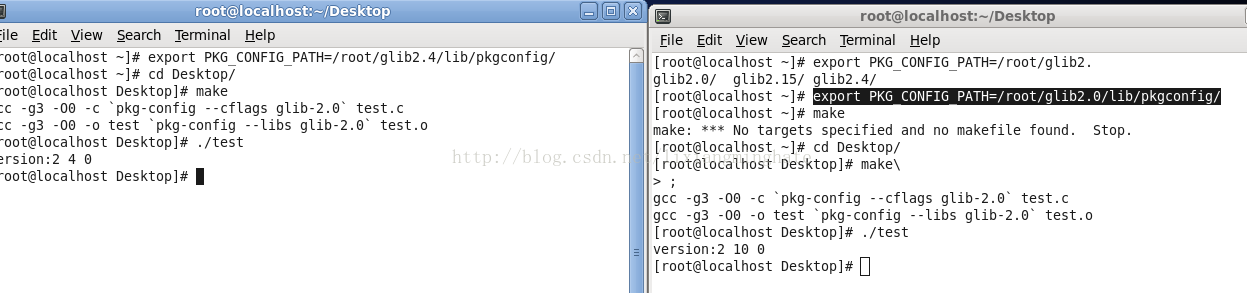
不同的搜索路径,得到不同的版本信息,这足以说明测试程序正确的连接了指定的glib版本。感觉这像是编译连接时的多态。

