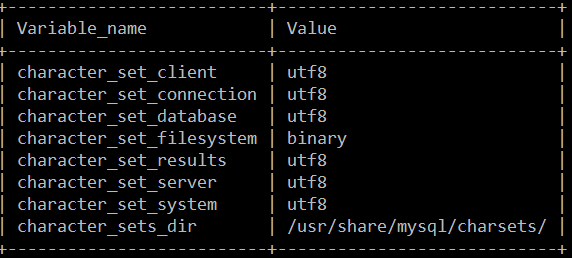
环境:
虚拟机:VMware Workstation 12 Pro
Linux发行版:Ubuntu 16.04.1 LTS (GNU/Linux 4.4.0-47-generic x86_64)
关于安装Mysql的方式采用此文中的在线安装方式:http://www.linuxdiyf.com/linux/26008.html。
本文旨在解决的问题:
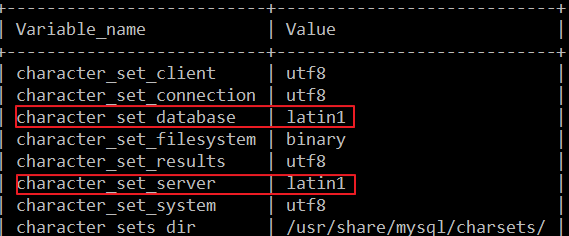
将Linux中的MySql编码从latin1:
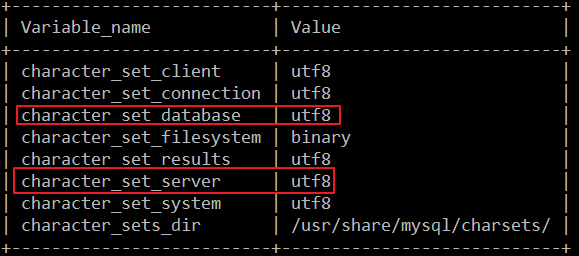
变为utf8:
分析Mysql启动时加载配置文件的顺序:
执行mysql --help命令,在输出的信息中我们可以看到这个描述:

此描述说明了,Mysql加载配置文件的顺序是
/etc/my.cnf -> /etc/mysql/my.cnf -> ~/.my.cnf
并且后面的文件的配置会覆盖前面的配置。
我们打开/etc/mysql/my.cnf这个文件,发现这个文件里除了注释就只有两条语句如下:
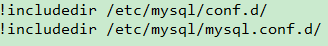
这说明Mysql会加载这两个目录下的所有 .cnf 结尾的文件。
我们打开/etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d目录发现有如下文件:
我们打开mysqld.cnf文件,发现里面的内容就是这对Mysql服务器端设置的内容,开头的内容如下:

从这段描述中我们可以知道,我们可以把这里面的内容全部复制到/etc/mysql/my.cnf中将其作为全局选项使用。
故有了解决方案:
首先我们打开/etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf文件,将其内容复制到/etc/mysql/my.cnf文件中,注意要保留/etc/mysql/my.cnf文件中原有的两条语句。
然后注释掉新的/etc/mysql/my.cnf文件中的!includedir /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/语句。
然后在新的/etc/mysql/my.cnf文件中的[mysqld]的下方加上此语句character-set-server=utf8,同时找到server-id选项将其注释去掉。
一个全新的完整的/etc/mysql/my.cnf文件如下:
#
# The MySQL database server configuration file.
#
# You can copy this to one of:
# - "/etc/mysql/my.cnf" to set global options,
# - "~/.my.cnf" to set user-specific options.
#
# One can use all long options that the program supports.
# Run program with --help to get a list of available options and with
# --print-defaults to see which it would actually understand and use.
#
# For explanations see
# http://dev.mysql.com/doc/mysql/en/server-system-variables.html
#
# This will be passed to all mysql clients
# It has been reported that passwords should be enclosed with ticks/quotes
# escpecially if they contain "#" chars...
# Remember to edit /etc/mysql/debian.cnf when changing the socket location.
#
# Here is entries for some specific programs
# The following values assume you have at least 32M ram
#
[mysqld_safe]
socket = /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock
nice = 0
#
[mysqld]
# The default character set that will be used when a new schema or table is
# created and no character set is defined
character-set-server=utf8
#
# * Basic Settings
#
user = mysql
pid-file = /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid
socket = /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock
port = 3306
basedir = /usr
datadir = /var/lib/mysql
tmpdir = /tmp
lc-messages-dir = /usr/share/mysql
skip-external-locking
#
# Instead of skip-networking the default is now to listen only on
# localhost which is more compatible and is not less secure.
bind-address = 127.0.0.1
#
# * Fine Tuning
#
key_buffer_size = 16M
max_allowed_packet = 16M
thread_stack = 192K
thread_cache_size = 8
# This replaces the startup script and checks MyISAM tables if needed
# the first time they are touched
myisam-recover-options = BACKUP
#max_connections = 100
#table_cache = 64
#thread_concurrency = 10
#
# * Query Cache Configuration
#
query_cache_limit = 1M
query_cache_size = 16M
#
# * Logging and Replication
#
# Both location gets rotated by the cronjob.
# Be aware that this log type is a performance killer.
# As of 5.1 you can enable the log at runtime!
#general_log_file = /var/log/mysql/mysql.log
#general_log = 1
#
# Error log - should be very few entries.
#
log_error = /var/log/mysql/error.log
#
# Here you can see queries with especially long duration
#log_slow_queries = /var/log/mysql/mysql-slow.log
#long_query_time = 2
#log-queries-not-using-indexes
#
# The following can be used as easy to replay backup logs or for replication.
# note: if you are setting up a replication slave, see README.Debian about
# other settings you may need to change.
server-id = 1
#log_bin = /var/log/mysql/mysql-bin.log
expire_logs_days = 10
max_binlog_size = 100M
#binlog_do_db = include_database_name
#binlog_ignore_db = include_database_name
#
# * InnoDB
#
# InnoDB is enabled by default with a 10MB datafile in /var/lib/mysql/.
# Read the manual for more InnoDB related options. There are many!
#
# * Security Features
#
# Read the manual, too, if you want chroot!
# chroot = /var/lib/mysql/
#
# For generating SSL certificates I recommend the OpenSSL GUI "tinyca".
#
# ssl-ca=/etc/mysql/cacert.pem
# ssl-cert=/etc/mysql/server-cert.pem
# ssl-key=/etc/mysql/server-key.pem
!includedir /etc/mysql/conf.d/
#!includedir /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/
查看mysql编码问题是否解决:
重启mysql服务,使用service mysql restart命令。
然后连接到mysql,使用mysql -u root -p命令,然后输入密码成功连接到mysql。
输入show variables like "chara%";命令查看到如下图所示结果表示成功修改了mysql的默认编码: