Description
The distributed operation layer (DOL) is a framework that enables the (semi-) automatic mapping of applications onto the multiprocessor SHAPES architecture platform. The DOL consists of basically three parts:
DOL Application Programming Interface: The DOL defines a set of computation and communication routines that enable the programming of distributed, parallel applications for the SHAPES platform. Using these routines, application programmers can write programs without having detailed knowledge about the underlying architecture. In fact, these routines are subject to further refinement in the hardware dependent software (HdS) layer.
DOL Functional Simulation: To provide programmers a possibility to test their applications, a functional simulation framework has been developed. Besides functional verification of applications, this framework is used to obtain performance parameters at the application level.
DOL Mapping Optimization: The goal of the DOL mapping optimization is to compute a set of optimal mappings of an application onto the SHAPES architecture platform. In a first step, XML based specification formats have been defined that allow to describe the application and the architecture at an abstract level. Still, all the information necessary to obtain accurate performance estimates is contained.
How to install
本次实验环境在Linux下进行,建议使用虚拟机安装Ubuntu,目前Ubuntu16.04已出。此次实验所用版本为Ubuntu14.04,该版本相比16.04较为稳定一些,可根据自己的需求下载。
安装必要环境
进入Ubuntu下,打开终端<Ctrl+Alt+t>,依次输入以下指令
$sudo apt-get update
$sudo apt-get install ant
$sudo apt-get install openjdk-7-jdk
$sudo apt-get install unzip
安装及更新有时会比较慢,主要是由于网速的原因,需要耐心等待。
下载文件
这里提供两个方法进行文件下载:
进入Ubuntu,打开终端<Ctrl+Alt+t>,输入以下指令
$sudo wget http://www.accellera.org/images/downloads/standards/systemc/systemc-2.3.1.tgz
$sudo wget http://www.tik.ee.ethz.ch/~shapes/downloads/dol_ethz.zip
可先将文件下载到本地电脑,再通过虚拟机与主机直接粘贴复制文件的方法将本地文件拷贝到虚拟机。
本次实验选择了第二种方法,第一种由于网速原因,下载速度过慢。在此也推荐使用第二种方法,如果以后需要拷贝文件到虚拟机也会方便很多。
解压文件
新建dol文件夹:<$ mkdir dol>
将下载的文件dol_ethz.zip解压到dol文件夹中:<$ unzip dol_ethz.zip -d dol>
解压systemc:<$ tar -zxvf systemc-2.3.1.tgz>
编译systemc
解压后进入systemc-2.3.1的目录下:<$ cd systemc-2.3.1>
新建一个临时文件夹objdir:<$ mkdir objdir>
进入该文件夹objdir:<$ cd objdir>
运行configure(能根据系统的环境设置一下参数,用于编译):<$ ../configure CXX=g++ --disable-async-updates>
成功时的显示如图:
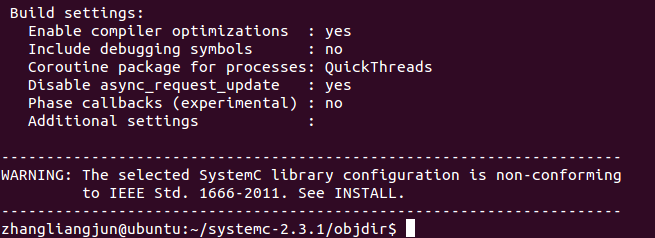
进行编译:<$ sudo make install>
成功时显示如图:
编译结束后,需要返回到systemc-2.3.1的目录下,并记录当前的工作目录,需要记录下来,在后面会用到:<$ cd ..> <$ pwd>
成功时显示如图:
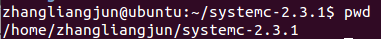
至此,systemc的编译就完成了。
编译DOL
进入刚刚的dol文件夹:<$ cd ../dol>
修改build_zip.xml文件,找到下面这段话,就是说上面编译的systemc位置在哪里,
<property name="systemc.inc" value="YYY/include"/>
<property name="systemc.lib" value="YYY/lib-linux/libsystemc.a"/>>
把YYY改成上页pwd的结果(注意,对于64位系统的机器,lib-linux要改成lib-linux64)
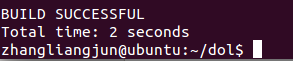
编译<$ ant -f build_zip.xml all>,若是成功,会显示build successful.
成功时显示如图:
至此,DOL的配置就结束了,但是我们还不知道这个配置到底有没有成功,如果配置这么久再不成功,那就悲剧了,这里我们只需要小小的测试一下就可以知道是否成功。
测试是否配置成功
进入build/bin/mian路径下:<$ cd build/bin/main>
运行第一个例子:<$ ant -f runexample.xml -Dnumber=1>
成功时如图所示:
如果最后显示”BUILD SUCCESSFUL”和”Total time:XXX seconds”。祝贺你,配置成功了。
Experimental experience
此次实验在Ubuntu环境下进行完成,由于已经安装并配置好了该环境,所以省去了一部分时间。在进行DOL配置时,还是出现了很多问题,通过查询网上的一些解决办法也是可以解决的。实验中最大的体会是在终端键入指令时,一定要仔细仔细再仔细,一个字母的错误都可能会让自己花费更多的时间去debug,配置环境时可能会出现各种各样的问题,问问已经配置好的小伙伴也是一种很好的选择,也能节约一点时间。

