LINUX下遍历目录的核心头文件是#include <dirent.h>,方法一般是这样的:打开目录->读取->关闭目录。相关函数有:DIR *opendir(const char *dirname);struct dirent *readdir(DIR *dirp);int closedir(DIR *dirp);注意到,在读取的时候,是返回一个叫dirent的结构体,其定义是这样的:
struct dirent{
long d_ino; /* inode number */
off_t d_off;/* offset to this dirent */
unsigned short d_reclen;/* length of this d_name */
char d_name [NAME_MAX+1]; /* file name (null-terminated) */
}
结构体中d_ino存放的是该文件的结点数目,什么是结点数目呢,我也说不清楚了,呵呵,d_off是文件在目录中的编移,具体是什么意思我也不是很明白,很少用,其本上就是用到:short d_reclen是这个文件的长度,需要注意的是这里的长度并不是指文件大小,因为大小和长度是2回事了,你可以用lseek将文件长度移得很长,但大小其实还是那么大,不过一般情况下,可以视为相同。最后一个元素就是我们要的了,文件名称!
而判断一个文件是文件还是文件夹则用到#include <sys/stat.h>这个文件,同样有一个stat的结构体,struct stat这个结构体是用来描述一个linux系统文件系统中的文件属性的结构。通过函数:int stat(const char *path, struct stat *struct_stat);将路径与这个结构体链接起来,再判断是否路径。struct stat这个结构体具体如下:
struct stat{
mode_t st_mode; //文件对应的模式,文件,目录等
ino_t st_ino; //inode节点号
dev_t st_dev; //设备号码
dev_t st_rdev; //特殊设备号码
nlink_t st_nlink; //文件的连接数
uid_t st_uid; //文件所有者
gid_t st_gid; //文件所有者对应的组
off_t st_size; //普通文件,对应的文件字节数
time_t st_atime;//文件最后被访问的时间
time_t st_mtime;//文件内容最后被修改的时间
time_t st_ctime;//文件状态改变时间
blksize_t st_blksize; //文件内容对应的块大小
blkcnt_t st_blocks; //文件内容对应的块数量
};
那么具体怎么用呢?下面用一个例子说明问题,程序具体完成的功能如下:
有如下的一个文件夹:
用户运行程序,第一个参数指定这个文件夹,就将这个文件夹遍历出来,同时打印文件长度,并且判断这个文件夹是目录还是文件。

同时还要注意,用户在路径末端有/或者没有/都是可以执行的:
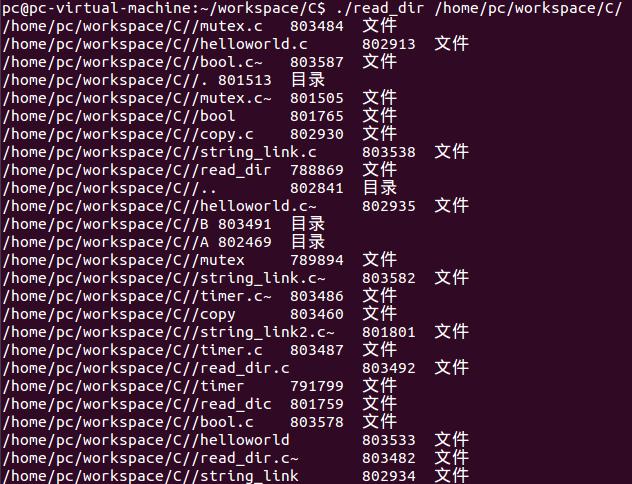
具体的代码如下,其中用到除了上述的内容以外,还说明了main参数如何用,唯一需要强调一下char* argv[]这个字符串输入中,第0个位置argv[0]是程序名,也就是上面的./read_dic,第1个位置argv[1]才是用户输入的第一个参数。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <dirent.h>//输出文件信息
#include <sys/stat.h>//判断是否目录
#include <string.h>
int is_dir(char* path){//判断是否是目录
struct stat st;
stat(path,&st);
if(S_ISDIR(st.st_mode)){
return 1;
}
else{
return 0;
}
}
char* str_contact(const char* str1,const char* str2){//字符串连接
char* result;
result=(char*)malloc(strlen(str1)+strlen(str2)+1);//str1的长度+str2的长度+\0;
if(!result){//如果内存动态分配失败
printf("字符串连接时,内存动态分配失败\n");
exit(1);
}
strcat(result,str1);
strcat(result,str2);//字符串拼接
return result;
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){//遍历整个目录
char* path=argv[1];//取用户输入的第一个参数
argv[1]=str_contact(argv[1],"/");//在后面补个/
DIR* dp;//用DIR指针指向这个文件夹
struct dirent* filename;
dp=opendir(path);
if(!dp){
printf("打开文件夹失败!\n");
return 0;
}
while(filename=readdir(dp)){//遍历DIR指针指向的文件夹,也就是文件数组。
char* path=argv[1];
path=str_contact(path,filename->d_name);//取文件名与当前文件夹拼接成一个完整的路径
if(is_dir(path)){
printf("%s\t%ld\t目录\n",path,filename->d_ino);
}
else{
printf("%s\t%ld\t文件\n",path,filename->d_ino);
}
}
closedir(dp);
return 0;
}

