sudo hdparm -B /dev/sda 可见硬盘/dev/sda的APM_level值为254,表示硬盘性能最大化,这需要保持高水平的硬盘转速,硬盘发热量自然就大.
如果返回/dev/sda: APM_level = not supported,则表示你的硬盘不支持APM(高级电源管理).
APM_level的全称为Advanced Power Management level,即(硬盘)高级电源管理级别.
man hdparm 可见:
Get/set Advanced Power Management feature, if the drive supports it.
A low value means aggressive power management and a high value means better performance.
Possible settings range from values 1 through 127 (which permit spin-down), and values 128 through 254 (which do not permit spin-down).
The highest degree of power management is attained with a setting of 1, and the highest I/O performance with a setting of 254.
A value of 255 tells hdparm to disable Advanced Power Management altogether on the drive (not all drives support disabling it, but most do).
该值的取值范围为1~255,值越大,硬盘性能越高,其中255表示关闭硬盘/dev/sda的电源管理,254表示在开启电源管理下的最高性能,1表示最低的硬盘性能但最省电.
这个值在1~127区间时允许spin-down,在128~254这个区间则禁止spin-down.
spin-down是指在闲置时挂起硬盘,停止转动,但是频繁的spin-down和spin-up会使硬盘寿命变短.
所以,即使你追求节能,减少发热量,也建议你将该值设为128,执行以下命令即可:
sudo hdparm -B 128 /dev/sda
我的操作系统为Ubuntu 14.04(Kernel 3.14),我把该值设为128,在气温26度的情况下,硬盘温度仅为36度(对比:此时CPU温度为39度).
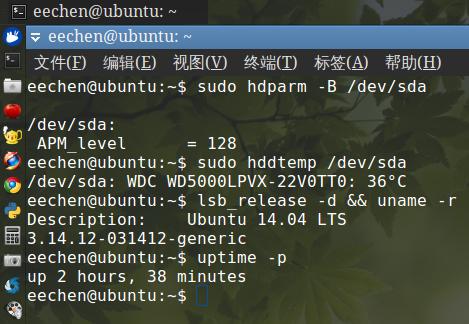
如果设为254,硬盘温度甚至会攀升到45度,虽然这仍是一个正常的硬盘温度,但对于笔记本用户来说,靠近硬盘处的发热量是很容易察觉到的.
另外电机持续高速的旋转也会加快减少硬盘的寿命.
在性能和节能间做个折中,个人把APM_level设为192,让其开机自动设置,在/etc/rc.local中加入:
hdparm -B 192 /dev/sda
如果/etc/rc.local不生效,可以在/etc/hdparm.conf中加入:
/dev/sda {
apm = 192
apm_battery = 192
}
apm表示在交流电供电模式下, apm_battery表示在电池供电模式下.
注意:设置APM后执行以下命令查看Load_Cycle_Count值
sudo smartctl -a /dev/sda | grep Load_Cycle_Count
如果Load_Cycle_Count值每分钟都在增加,这时你应该把APM值设回原来的254,方法同上可以在/etc/hdparm.conf里修改.
执行命令 sudo hdparm -B 254 /dev/sda 即时生效, 配置在重启后生效.
因为磁头频繁的Load/Unload同样会影响硬盘寿命,一般硬盘设计能承受的加载循环计数Load_Cycle_Count最多为600000次.
T400 thinkpad安装了ubuntu 12.10很卡,发热大的断电:http://www.linuxdiyf.com/linux/14365.html
解决Ubuntu Linux发热的问题:http://www.linuxdiyf.com/linux/9866.html
安装Bumblebee解决Ubuntu笔记本发热量大问题:http://www.linuxdiyf.com/linux/2955.html
Ubuntu 12.04发热超级厉害解决方法:http://www.linuxdiyf.com/linux/2389.html

