正则表达式:它是指一个用来描述或者匹配一系列符合某个句法规则的字符串的单个字符串。在很多文本编辑器或其他工具里,正则表达式通常被用来检索或替换那些符合某个模式的文本内容。
其实正则表达式,只是一种思想,一种表示方法。只要我们使用的工具支持表示这种思想那么这个工具就可以处理正则表达式的字符串。常用的工具有grep, sed, awk,这三个都是针对文本的行才操作的。
grep 过滤器
语法: grep [-cinvABC] 'word' filename
-n 显示行号
-c count统计符合要求的行数
-v 取反,不包含所选字符的
-i 不区分大小写
-r 会把目录下面所有的文件遍历 例如: grep -r 'root' ./
-A 后面跟数字,A2表示打印符合要求的行及下面二行
-B 后面跟数字,B2表示打印符合要求的行及上面二行
-C 后面跟数字,C2表示打印符合要求的行及上下各二行
^ 行首,开头
$ 行尾,结尾
空行用 ^$ 表示
可以做一个别名alias grep="grep --color" 写入到.bashrc里面;以后输入grep命令时查找的关键字符会颜色显示,方便区分。
过滤带有某个关键词的行并输出行号,颜色显示关键词
[root@localhost ~]# grep -n --color 'root' passwd
1:root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
11:operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
[root@localhost ~]# grep -o --color 'root' passwd | wc -l
4
加-o 统计包含关键词的个数;
过滤不带有某个关键词的行,并输出行号;
[root@yonglinux ~]# grep -nv 'nologin' /etc/passwd
1:root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
6:sync:x:5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync
7:shutdown:x:6:0:shutdown:/sbin:/sbin/shutdown
8:halt:x:7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt
20:user1:x:600:501::/home/user1:/bin/bash
23:mysql:x:27:27:MySQL Server:/var/lib/mysql:/bin/bash
过滤以nologin结尾的,系统禁止登陆的所有用户;
[root@localhost ~]# grep 'nologin$' /etc/passwd
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin
lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin
mail:x:8:12:mail:/var/spool/mail:/sbin/nologin
uucp:x:10:14:uucp:/var/spool/uucp:/sbin/nologin
示例,打印关键字halt所在行的A2 B2 C2
[root@yonglinux ~]# grep -A2 'halt' passwd
halt:x:7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt
mail:x:8:12:mail:/var/spool/mail:/sbin/nologin
uucp:x:10:14:uucp:/var/spool/uucp:/sbin/nologin
[root@yonglinux ~]# grep -B2 'halt' passwd
sync:x:5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync
shutdown:x:6:0:shutdown:/sbin:/sbin/shutdown
halt:x:7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt
[root@yonglinux ~]# grep -C2 'halt' passwd
sync:x:5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync
shutdown:x:6:0:shutdown:/sbin:/sbin/shutdown
halt:x:7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt
mail:x:8:12:mail:/var/spool/mail:/sbin/nologin
uucp:x:10:14:uucp:/var/spool/uucp:/sbin/nologin
把所有以#号开头的行去除
[root@yonglinux ~]# grep -v '^#' /etc/inittab
id:3:initdefault:
去除所有空行和以#号开头的行
[root@yonglinux ~]# grep -v '^#' /etc/crontab |grep -v '^$'
SHELL=/bin/bash
PATH=/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin
MAILTO=root
HOME=/
示例说明,打印数字或字母开头,及不是字母和数字开头的;
[root@yonglinux tmp]# cat test.txt
helloworld
abc
abc11111
#differt
12345
67899
123def
[0-9]代表任意一个数字,整个命令意思筛选出包含任意一个数字的行;
[root@yonglinux tmp]# grep '[0-9]' test.txt
abc11111
12345
67899
123def
[^0-9]代表除0-9之外的任意一个字符,整个命令的意思是筛选出不包含数字的行;
[root@yonglinux tmp]# grep '[^0-9]' test.txt
helloworld
abc
abc11111
#differt
123def
^[^0-9]代表不是数字开头的;
[root@yonglinux tmp]# grep '^[^0-9]' test.txt
helloworld
abc
abc11111
#differt
[a-z]代表任意一个英文字母;
[root@yonglinux tmp]# grep '[a-z]' test.txt
helloworld
abc
abc11111
#differt
123def
[^a-z]代表除英文字母以外的;
[root@yonglinux tmp]# grep '[^a-z]' test.txt
abc11111
#differt
12345
67899
123def
^[^a-z]代表不是英文字母开头的文本;
[root@yonglinux tmp]# grep '^[^a-z]' test.txt
#differt
12345
67899
123def
[ ] 如果是数字的话就用[0-9]这样的形式,当然有时候也可以用这样的形式[15]即只含有1或者5,注意,它不会认为是15。如果要过滤出数字以及大小写字母则要这样写[0-9a-zA-Z]。另外[ ]还有一种形式,就是[^字符] 表示除[ ]内的字符之外的字符。
过滤任意一个字符与重复字符
[root@yonglinux ~]# grep 'h..t' /etc/passwd
halt:x:7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt
'.'点表示任意的一个字符,上面例子为把符合h与t之间有2个任意字符的行过滤出来。
'*'代表零个或多个任意的字符
'ooo*'代表oo,ooo,oooo 或者更多的o
[root@yonglinux ~]# grep 'ooo*' /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin
mail:x:8:12:mail:/var/spool/mail:/sbin/nologin
uucp:x:10:14:uucp:/var/spool/uucp:/sbin/nologin
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
postfix:x:89:89::/var/spool/postfix:/sbin/nologin
'.*'表示零个或多个任意字符,等于所有的,空行也包含在内。
[root@yonglinux ~]# grep '.*' /etc/passwd |wc -l
24
[root@yonglinux ~]# wc -l /etc/passwd
24 /etc/passwd
指定要过滤字符出现的次数
{ }内部为数字,表示前面字符要重复的次数。表示两个O即包含OO的行。{ }左右都需要加脱意字符\
grep -E 代表增强版的grep即egrep,使用egrep不需要脱意;
123456789 [root@yonglinux ~]# grep 'o\{2\}' /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin
mail:x:8:12:mail:/var/spool/mail:/sbin/nologin
uucp:x:10:14:uucp:/var/spool/uucp:/sbin/nologin
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
postfix:x:89:89::/var/spool/postfix:/sbin/nologin
[root@localhost ~]# grep -E 'o{2}' passwd
[root@localhost ~]# egrep 'o{2}' passwd
[root@yonglinux ~]# cat test.txt
root:hot
abcde
spoool
spool
spol
spl
示例,过滤字母o出现1到3次的行
[root@yonglinux ~]# grep 'o\{1,3\}' test.txt
root:hot
spoool
spool
spol
{ } 还可以表示一个范围,格式为{n1,n2} n1<n2 表示重复n1到n2次前面的字符,n2还可以为空,则表示大于等于n1次。
egrep为grep的扩展版本,我们可以用egrep完成grep不能完成的工作,当然了grep能完成的egrep完全可以完成。
grep -E = egrep
1、筛选一个或一个以上前面的字符 字符后面使用+
[root@yonglinux ~]# cat test.txt
rot:x:0:0:rot:/rot:/bin/bash
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
rooooot:x:0:0/roooooot:/bin/bash
11111111111111111111111111111111
aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
[root@yonglinux ~]# egrep 'o+' test.txt
rot:x:0:0:rot:/rot:/bin/bash
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
rooooot:x:0:0/roooooot:/bin/bash
[root@yonglinux ~]# egrep 'oo+' test.txt
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
rooooot:x:0:0/roooooot:/bin/bash
[root@yonglinux ~]# egrep 'ooo+' test.txt
rooooot:x:0:0/roooooot:/bin/bash
2、筛选零个或一个前面的字符 字符后面使用?
[root@yonglinux ~]# egrep 'o?' test.txt
rot:x:0:0:rot:/rot:/bin/bash
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
rooooot:x:0:0/roooooot:/bin/bash
11111111111111111111111111111111
aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
[root@yonglinux ~]# egrep 'oo?' test.txt
rot:x:0:0:rot:/rot:/bin/bash
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
rooooot:x:0:0/roooooot:/bin/bash
[root@yonglinux ~]# egrep 'ooo?' test.txt
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
rooooot:x:0:0/roooooot:/bin/bash
[root@yonglinux ~]# egrep 'oooo?' test.txt
rooooot:x:0:0/roooooot:/bin/bash
3、筛选字符串1或字符串2 包含里面任意一个字符串的打印出来
[root@yonglinux ~]# egrep 'aaa|111|ooo' test.txt
rooooot:x:0:0/roooooot:/bin/bash
11111111111111111111111111111111
aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
4、egrep中()的应用
[root@yonglinux ~]# egrep 'r(oo)|(mo)n' test.txt
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
rooooot:x:0:0/roooooot:/bin/bash
用( )表示一个整体,例如(oo)+ 表示1个'oo'或者多个'oo'
[root@yonglinux ~]# egrep '(oo)+' test.txt
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
rooooot:x:0:0/roooooot:/bin/bash
5、egrep中[ ]的应用
方括号内的字符为其中的一个;[^o]为除了字母o之外的;
示例:r开头t结尾的;;
[root@localhost ~]# egrep 'r[o]t' test.txt
rot:x:0:0:rot:/rot:/bin/bash
r开头后面有o的
[root@localhost ~]# egrep 'r[o]' test.txt
rot:x:0:0:rot:/rot:/bin/bash
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
rooooot:x:0:0/roooooot:/bin/bash
r开头后面不是o的;
[root@localhost ~]# egrep 'r[^o]' test.txt
rrt
rtx
t为结尾的前面字符不是o的;
[root@localhost ~]# egrep '[^o]t' test.txt
rrt
rtx
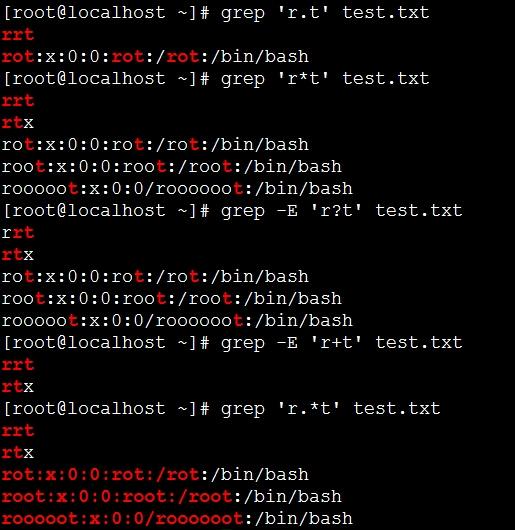
. * + ? 符号的总结
. 表示任意一个字符(包括特殊字符 空格 # $ ?)
* 表示零个或多个*前面的字符
.* 表示任意个任意字符(包含空行)
+ 表示1个或多个+前面的字符
? 表示0个或1个?前面的字符
其中,+ ? grep不支持,egrep才支持。
"ro.*t" 表示以ro开头一直到t结尾的
[root@localhost ~]# grep 'ro.*t' test.txt
rot:x:0:0:rot:/rot:/bin/bash
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
rooooot:x:0:0/roooooot:/bin/bash
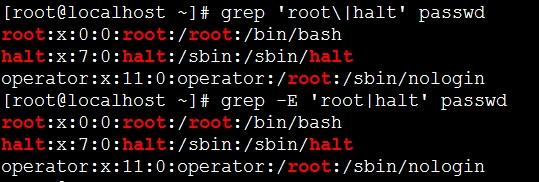
grep如果需要筛选字符串 | 管道需要加脱意\才可以使用;
注:以上图片上传到红联Linux系统教程频道中。